Highlights:
|
Jump to ↓
Among the most promising applications for Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) is in Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) compliance and reporting for large businesses.
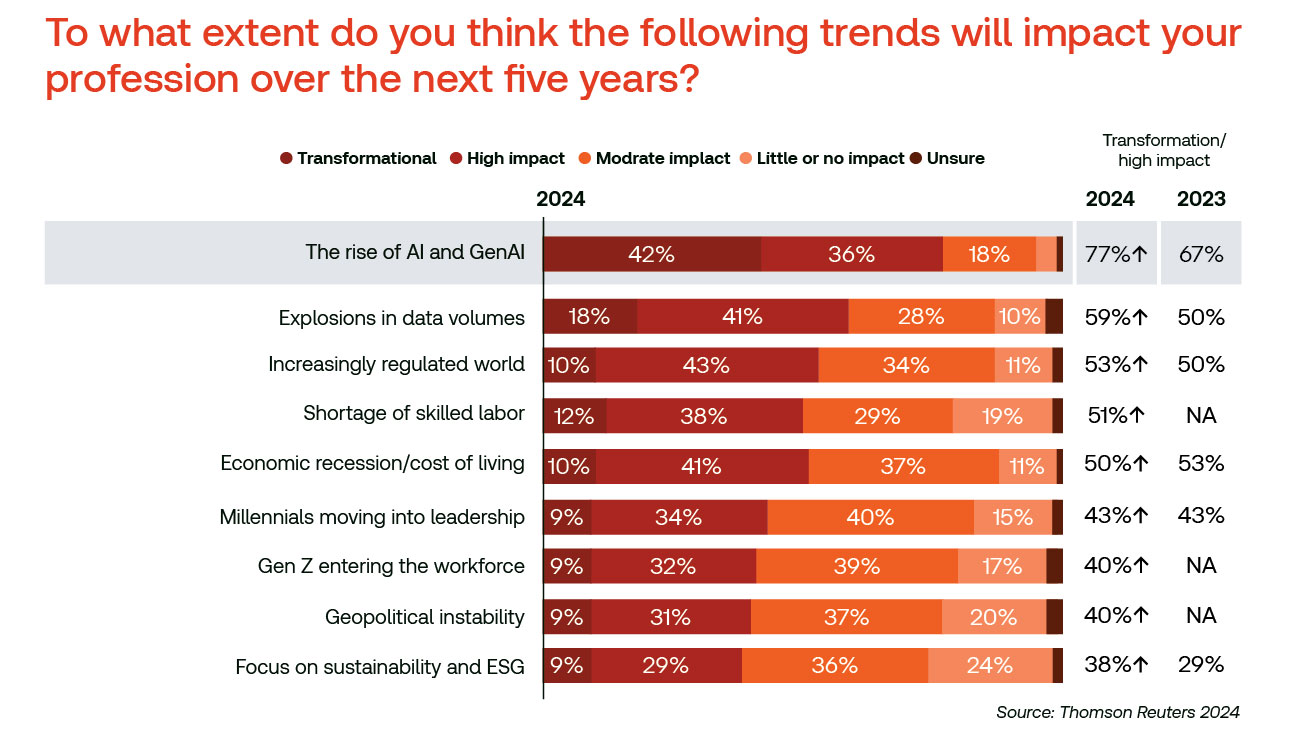
As the demand for ESG-related data rapidly expands and compliance teams spend more and more of their time on ESG initiatives, GenAI-enabled software solutions offer a way to ensure compliance, save time, and provide companies with a competitive advantage in the increasingly important business arena that ESG compliance has become. According to the Thomson Reuters 2024 State of Corporate ESG Report, 77% of survey respondents said they believe AI will have a high or transformational impact on their work over the next five years.
ESG’s importance—and data demands—are growing
In today’s business world, a corporation’s reputation (to say nothing of its stock price) is increasingly tied to its ability to meet various ESG targets—some self-imposed and others required by law.
Everything from a company’s energy efficiency, water usage, and waste-management practices to its labor policies, product safety measures, and governance rules are covered under most corporate ESG programs. And once a company commits itself to a set of ESG standards, an enormous audience of interested parties—e.g., shareholders, consumers, regulators, activists, media—is inevitably watching to make sure the company fulfills its promises.
Unfortunately, as regulatory scrutiny increases, data demands multiply, and the consequences of non-compliance become more serious and costly, those responsible for ensuring ESG compliance (primarily ESG compliance teams, CFOs, tax and finance professionals) are being overwhelmed with ESG-related busywork.
It takes considerable resources (time, money, human capital) to collect, store, and analyze the increasingly large amounts of data that ESG compliance requires. Ensuring the consistency and reliability of that data throughout the supply chain also involves technological resources that many companies still lack.
Complicating matters further is the fact that the regulatory landscape around ESG is constantly changing. For example, the European Union (EU) recently passed its long-awaited Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), a wide-ranging mandate that significantly expands the scope and depth of ESG-related information that companies are required to disclose.
By 2026, all but the smallest companies operating in the EU will be subject to CSRD rules, and it is widely believed that the CSRD will soon serve as the framework for an emerging global standard on sustainability reporting.
How GenAI is transforming ESG management
GenAI is an ideal application for ESG compliance because it combines the speed of machine learning for data collection with GenAI’s ability to organize, analyze—and learn from—that same data.
ESG compliance processes typically involve a series of repeatable steps, many of which are easily automated. Once trained on a company’s ESG process, a GenAI-empowered ESG-compliance tool can free up human time and resources by speeding up key functions and automatically executing various steps in the compliance process.
For example, gathering ESG-related data on suppliers in an international supply chain can take more than a year, but GenAI-enabled software can accomplish the same task in less than a quarter of that time, creating a much more efficient procurement process. GenAI can also assist with such common ESG tasks as filling out audit reports, responding to customer data requests, managing certifications, and responding to ESG-related data requests from other departments, such as IT and finance.
In addition to creating more efficient processes and freeing up human resources, one of the most promising applications for GenAI is in assisting decision-makers through advanced data analysis and predictive modeling. By understanding a company’s ESG benchmarks and targets and comparing them with its current trajectory, GenAI can help companies understand their ESG profile at any given moment and identify areas in need of improvement.
Use cases for GenAI in ESG reporting and monitoring
For example, Enersys, a maker of next-gen batteries and other stored energy solutions, uses a version of ChatGPT Enterprise that analyzes sustainability metrics in ESG-related areas such as emissions, waste, and travel. Using that data, team members report uncovering actionable insights much more quickly than they could analyzing the data manually. Enersys’s system can also respond automatically to customer data requests and generate internal reports. Furthermore, the company’s sustainability team is exploring the idea of using GenAI to review its Climate Disclosure Project (CDP) questionnaire responses to identify data gaps and areas in need of improvement.
Strengthening auto supply chains
Another interesting use case for GenAI is automobile manufacturers who are transitioning to electric vehicles (EVs) and, in the process, significantly altering their supply chains. As mentioned earlier, GenAI can accelerate the process of new supplier screening and onboarding and can immediately flag any areas of possible concern.
During the auto industry’s turbulent transition to EVs, these onboarding efficiencies can help automakers maintain reliable, resilient supply chains. Advanced screening capabilities can also ensure that a manufacturer’s supply chain reflects the company’s values in terms of labor practices, sourcing of materials, energy efficiency, waste management, and other key ESG metrics.
 |
|
ESG standards: The key to long-term resilience
As these examples demonstrate, the growing demands of ESG-related data-collection and reporting are quickly making the use of GenAI-enabled tools essential for any organization that is serious about meeting its ESG obligations. Guaranteed compliance isn’t the only benefit, either. As regulatory pressures mount and stakeholder expectations evolve, companies that invest in robust ESG software solutions are positioning themselves for long-term resilience and strategic success in a rapidly changing world.
They may also be helping to save the world.
Let’s not forget, ESG initiatives were originally devised as a way for investors to distinguish between corporate entities that operate with sustainability, equality, and fairness in mind—and those who don’t. Companies that are serious about ESG compliance are sending a message to stakeholders that they care about these issues and are willing to do what it takes to meet their ESG obligations. Indeed, according to the Thomson Reuters 2024 State of Corporate ESG Report, 82% of respondents agreed that the role of corporate performance will grow in the future, and 71% agreed that their company is willing to invest in ESG to gain a competitive advantage.
Why GenAI is necessary to meet rising ESG demands
As climate change grows more volatile and political influence on supply chains becomes unavoidable, more companies than ever are viewing their ESG initiatives not only as an organizational responsibility, but as an excellent opportunity to strengthen and differentiate their brand.
Unfortunately, the process of ESG compliance has become so cumbersome and time-consuming that the people responsible for it are often overwhelmed. Keeping up with constant regulatory changes and the increasingly granular nature of ESG data requirements is difficult without the proper tools—the best of which are forms of GenAI-enhanced software developed by third-party providers that integrate seamlessly into a company’s existing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) platform.
In addition to ensuring compliance, GenAI-based ESG software can help companies streamline processes, generate efficiencies, improve accuracy, and free up staff time currently spent on mundane, low-value tasks. And, as these GenAI-powered programs “learn” a company’s business, they can also be used to help decision-makers model scenarios and develop plans for a more competitive and sustainable future.
For a more complete overview of how GenAI is impacting ESG compliance, download a free copy of the 2024 State of Corporate ESG Report.
 |
|
 |
|