Now that cryptocurrency and other related financial technologies have hit the mainstream, most people have heard of blockchains and may even have a working idea of what they do. But the world of tech evolves at breakneck speed, and a system like Hashgraph may also soon become part of the public lexicon.
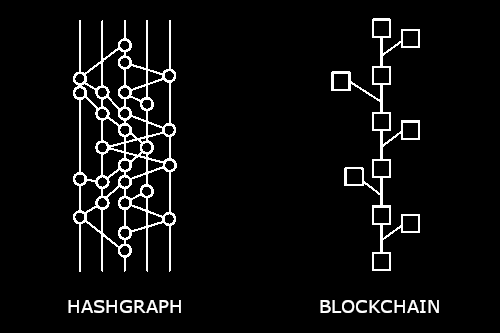
Blockchain and Hashgraph both fall under the umbrella of distributed ledger technologies, or technologies that allow their respective participants in the network to propose, validate, and update records of transactions in a fully synchronized way. Both are also being explored for their potential role in decentralized finance, where power over a transaction is shared equally among participants in the network and not exclusively held by one privileged party or intermediary.
But what distinguishes blockchain from Hashgraph, and what should you know about either system for keeping digital ledgers? Here’s a quick summary for those who are curious about blockchain’s and Hashgraph’s future implications.
A Briefer on Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology is what drives well-known cryptocurrency coins like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH). It is also the technology behind up-and-coming privacy coins like Monero (XMR) traded from an XMR wallet.
A blockchain uses cryptography to store incoming transactional records in eponymous “blocks.” These blocks eventually form whole chains that their owners can verify. Information held on any blockchain is immutable, or incapable of being altered or discarded once it’s been recorded.
The same cryptographic technology is also used to provide security for each block and make sure that all information stored in the blocks is safe from tampering. Simply put, blockchains utilize a linear approach for organizing and storing data from participating nodes, and that linear approach is what most crypto traders and miners are used to.
Hashgraph: A Formidable New Player in Digital Ledger Technology
Short for Hedera Hashgraph, Hashgraph is a relatively new player to the digital ledger game. Instead of using a block system like blockchain, Hashgraph technology uses a directed acyclic graph to sequence all transactions made on the network.
Of particular note is Hashgraph’s use of a protocol called “gossip about gossip,” which records the history of how participants have communicated within the network. The gossip about gossip protocol distributes new information to nodes in the network that have a history of the previous transaction. When more events transpire on the network, information circulates more quickly (which is not unlike real-life gossip from multiple sources).
Hashgraph is currently taking the financial technology industry by storm due to the incredible speed that it’s capable of. This system can handle up to thousands of complex transactions every second, and it can verify millions of signatures in under a minute. Its appeal has further broadened with the introduction of its own proprietary cryptocurrency, which is called HBAR. HBAR works in pretty much the same way that other crypto coins do, i.e. using a peer-to-peer system within its network.
The Key Differences between Blockchain and Hashgraph
There are three differences that should concern newcomers to both blockchain and Hashgraph. First is the freedom that participants have to refine the existing digital ledger infrastructure. Blockchain, which has been widely celebrated by early adopters of decentralized finance, runs on open-sourced distributed ledger infrastructure. That means that users can easily create their own cryptocurrencies and refine their own blockchains once they get acquainted with the base technology. Hashgraph, on the other hand, is privately held and runs on a patented algorithm from software platform Swirlds. Therefore, any new refinements to the technology have to be approved by Swirlds developers.
The second key difference lies in how the two technologies reach a consensus for their transactions. So far, blockchain has been known to utilize consensus algorithms like proof of stake, proof of work, proof of elapsed time, and practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance or pBFT for digital transactions to happen. On the other end of the spectrum, Hashgraph requires only virtual voting from its participants to achieve network consensus. This makes Hashgraph less resource-intensive on computational power and electricity than blockchain is.
The third difference is the speed at which transactions can be done on either technology. Hashgraph’s use of the gossip about gossip protocol makes it capable of validating as many as 500,000 transactions on its ledger every second. The general speed of transactions on a blockchain, however, depends on which blockchain is in question and which individual protocols the blockchain uses for implementation. But with a rate between 100 and 10,000 transactions per second, blockchain’s speed pales in comparison to what Hashgraph is capable of at its peak.
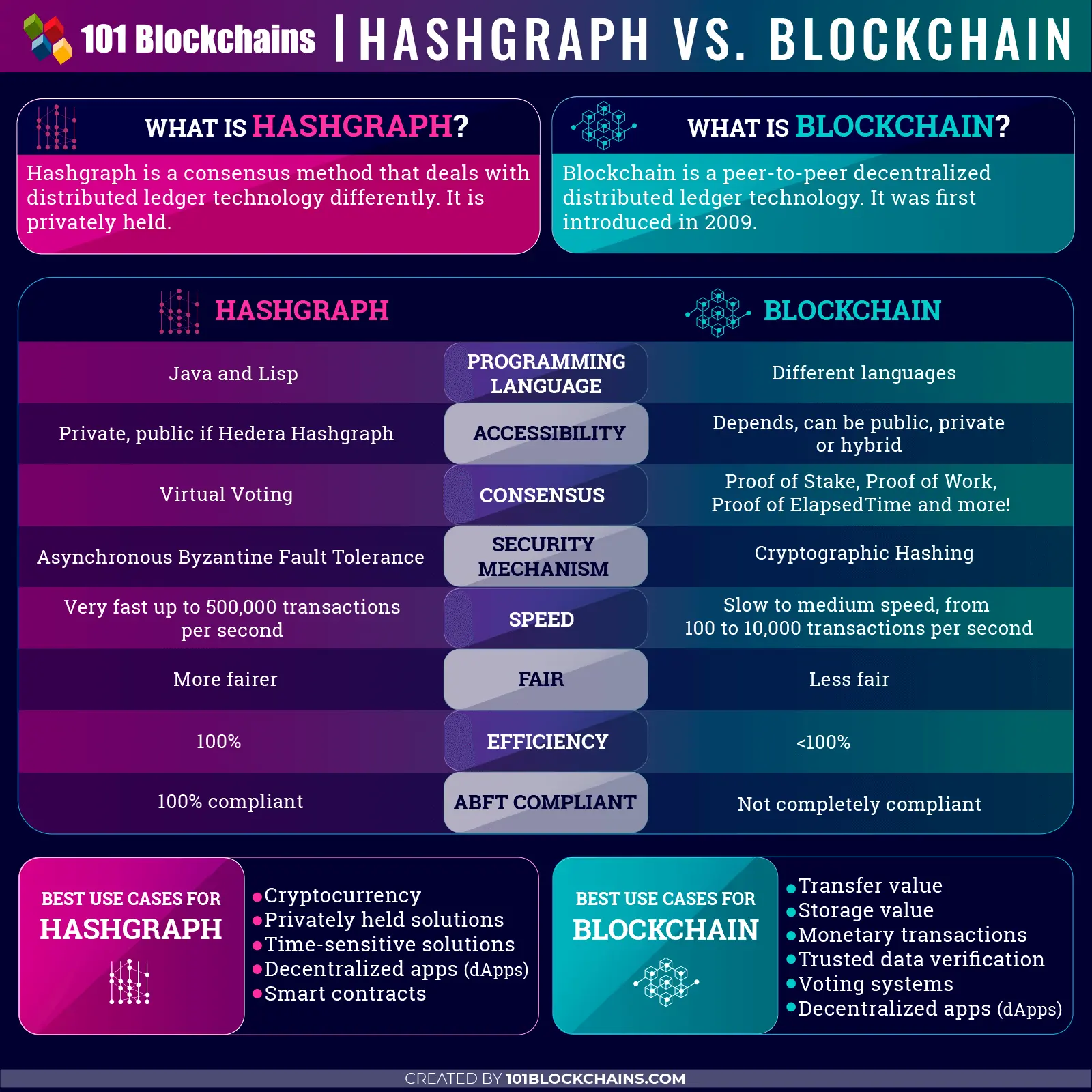
image credit: 101 Blockchains
Which of the Two Digital Ledger Technologies is Better?
On the question of which digital ledger technology is better than the other, the answer really depends on what solutions the users are after. Blockchain is definitely the more popular and more widely accepted digital ledger technology between the two, and it’s already being used for applications like supply chain management and smart contracts between companies in the finance industry. As of this time, blockchain can promise a shallower learning curve and a more universalized user experience compared to Hashgraph.
But there’s no denying that Hashgraph is making a splash in the fintech sector for its speed due to the gossip as gossip protocol, as well as its efficiency with resources. It may soon be adopted by more companies that want to invest in a digital ledger for time-sensitive solutions.
The world may still be in the process of learning about blockchain, but contending technologies also deserve equal attention. Watch out for industry updates on applications using either blockchain or Hashgraph, and imagine what kind of role either system could play in your personal financial matters.